オリーブオイルを日常摂取する事で、心血管疾患や冠状動脈性心臓病にかかるリスクを軽減されるデータ。
エキストラバージンオリーブオイルに含まれるポリフェノールや、オレイン酸が効いているのでは。
Abstract : Olive Oil Consumption and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
Background: Olive oil intake has been associated with lower risk of cardiometabolic risk factors in Mediterranean populations, but little is known about these associations in the U.S. population, where olive oil intake is relatively low.
Objectives: To examine whether olive oil intake is associated with total Cardiovascular Disease (CVD), coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke risk.(オリーブオイルの摂取が心血管疾患(CVD)、冠状動脈性心臓病(CHD)、脳卒中のリスク全体に関連しているかどうかを調べる。)
Methods: We included 63,867 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (1990 to 2014) and 35,512 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1990 to 2014) who were free of cancer, heart disease, and stroke at baseline. Diet was assessed using food frequency questionnaires at baseline and then every 4 years. Cumulative average of intake was used in the primary analysis. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to estimate hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals.
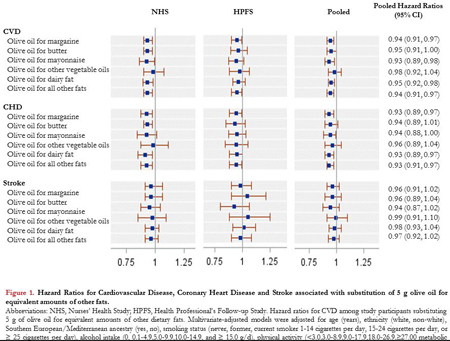
Results: During 24 years of follow-up, we documented 10,240 incident cases of CVD, including 6,270 CHD cases and 3,970 stroke cases. After adjusting for major diet and lifestyle factors, compared with non-consumers, those with higher olive oil intake (>1/2 tablespoon/d or > 7g/d) had 15% lower risk of total CVD (24年間の追跡期間中に、6,270件のCHD症例と3,970件の脳卒中症例を含む10,240件のCVDの発生症例を記録しました。 主要な食事とライフスタイルの要因を調整した後、非消費者と比較して、オリーブオイルの摂取量が多い人(> 1/2大さじ/日または> 7g /日)は、総CVDのリスクが15%低かった。)
[pooled hazard ratio (95% confidence interval): 0.85 (0.77, 0.93)] and 21% lower risk of CHD [pooled hazard ratio (95% confidence interval): 0.79 (0.70, 0.89)]. No significant associations were observed for total stroke or ischemic stroke. We estimated that replacing 5g of margarine, butter, mayonnaise, or dairy fat with the equivalent amount of olive oil was associated with 5-7% lower risk of total CVD and CHD. No significant associations were observed when olive oil was compared with other plant oils combined (corn, safflower, soybean and canola oil).
Conclusions: Higher olive oil intake was associated with a lower risk of CHD and total CVD in two large prospective cohorts of U.S. men and women. (オリーブオイルの摂取量が多いと、CHDと総CVDのリスクが低くなる事が米国の大規模な集団テストからわかった。)
引用URL:https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circ.141.suppl_1.P509

